Independent Living
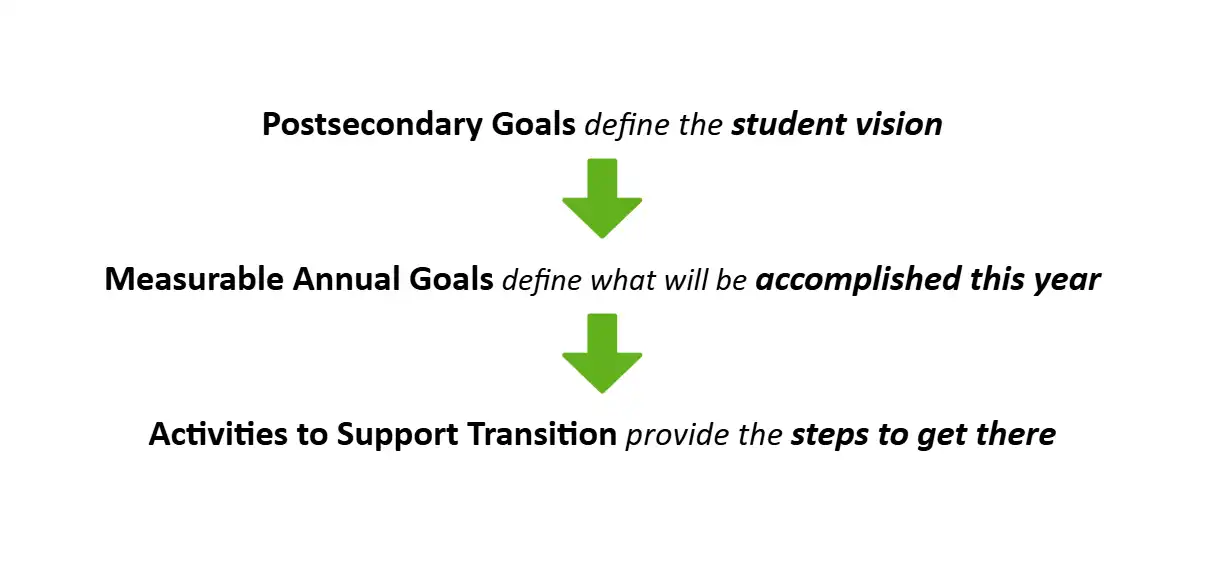
“Student Vision”
Example Postsecondary Independent Living Goals
“Student Vision”
“Student Vision”
General Examples:
- After high school, [Student] will live in an apartment with a roommate and manage personal finances with limited support.
- Following graduation, [Student] will use public transportation independently to get to work and social activities.
- Upon exiting school, [Student] will manage personal health care needs, including scheduling medical appointments and taking medications.
Extensive Support Needs Examples:
- After exiting school, [Student] will live in a supervised group home and participate in daily routines with staff support.
- Following graduation, [Student] will use a picture-based schedule and adult support to complete daily hygiene and meal preparation tasks.
- Upon leaving school, [Student] will use specialized transportation (paratransit) with assistance from a caregiver to access community services.
“What they will accomplish this year”
Example Measurable Annual IEP Goals: Independent Living
“What they will accomplish this year”
“What they will accomplish this year”
General Independent Living Goals:
- [Student] will create a monthly budget using a simple template and maintain it for at least 2 consecutive months with 80% accuracy.
- [Student] will independently plan, shop for, and prepare one simple meal per week using a checklist.
- [Student] will demonstrate safe pedestrian skills (e.g., crossing at crosswalks, reading signals) in community settings in 3 out of 4 trials.
Extensive Support Needs Independent Living Goals:
- Using a visual sequence, [Student] will complete a morning hygiene routine (e.g., brushing teeth, washing face) with no more than 2 prompts in 4 out of 5 trials.
- [Student] will use a picture schedule to complete a 3-step household chore (e.g., vacuuming, setting a table) in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
- With adult support, [Student] will use a communication device to choose between 2 transportation options (e.g., van or bus) in 4 out of 5 community outings.
“Steps to get there”
Activities to Support Transition: Independent Living
“Steps to get there”
“Steps to get there”
Staff will provide opportunities to explore community recreation and leisure resources and venues.
Instruction in consumer rights, cooking safety, and cost comparison strategies will be provided by staff.
Parent will provide opportunities for (NAME) to cook at home and to learn more about car maintenance.
The special education teacher will work with (NAME) to improve math skills related to personal banking and money management so she can live independently.
The occupational therapist will work with (NAME) on fine motor coordination so she can brush her own hair.
Teach cooking, cleaning, budgeting, and grocery shopping.
Practice using public transportation, reading schedules, and ride-sharing apps.
Cover budgeting, using a bank account, and paying bills.
Teach skills in natural settings (e.g., practicing shopping at a store).
Research and visit different living arrangements (group homes, supported apartments).
Promote self-care, medication management, and making medical appointments.
Encourage relationship-building, conflict resolution, and appropriate communication.
Teach basic tasks like microwaving meals, pouring liquids, or using adapted utensils, using visual recipes.
Use color-coded bins, tactile labels, and task cards to sort, wash, and fold clothes.
Reinforce consistent routines using sequencing charts, timers, and embedded OT/PT supports.
Practice using community transportation with step-by-step visual guides or video walk-throughs.
Create shopping lists with pictures; practice identifying and purchasing 1–3 items.
Safety Skills in the Community:
- Recognizing signs (e.g., “Stop,” “Exit”)
- Stranger awareness role-play
Follow step-by-step visuals or task boxes to complete routine chores.
Practice calling family, sending a picture message, or using a voice assistant for a task.
Explore adapted sports, music activities, or crafts with structured supports.
