Employment
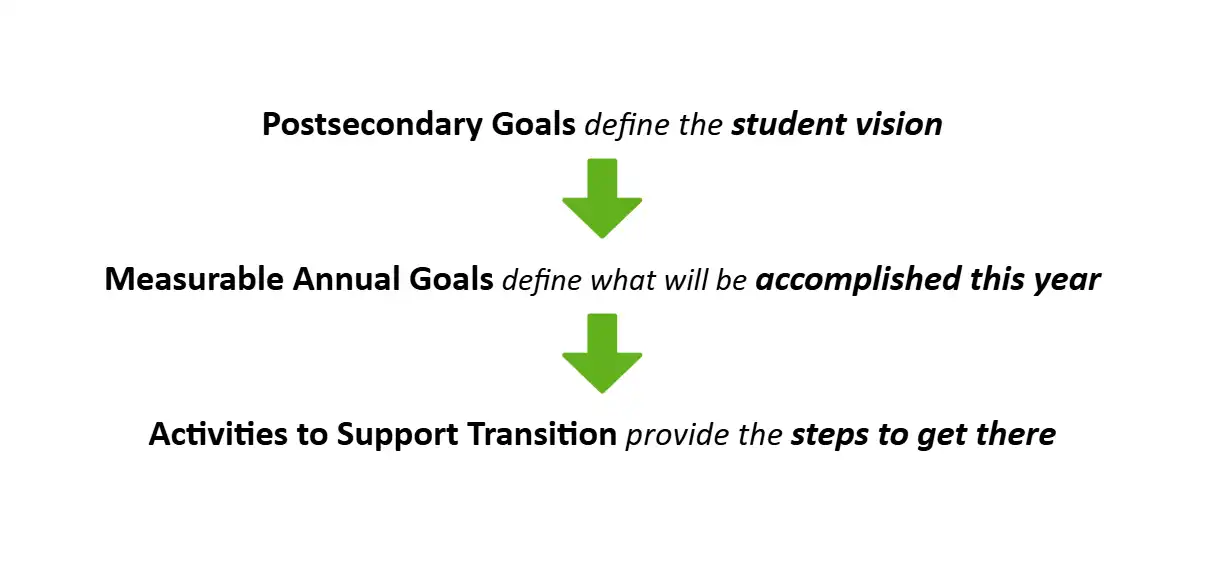
“Student Vision”
Example Postsecondary Employment Goals
“Student Vision”
“Student Vision”
General Examples:
- After high school, [Student] will obtain part-time employment in a retail environment such as a grocery or clothing store.
- Following graduation, [Student] will work full-time as an apprentice in a construction trade and pursue certification.
- After completing training, [Student] will secure a job as an administrative assistant at a local office.
Extensive Support Needs Examples:
- After graduation, [Student] will obtain supported employment in a local business setting, such as a laundromat or cafeteria, with assistance from a job coach.
- Following high school, [Student] will participate in a community-based work program that includes individualized employment opportunities with supervision.
- Upon exiting school, [Student] will engage in a structured volunteer or enclave employment setting 3–5 days per week with adult support.
“What they will accomplish this year”
Example Measurable Annual IEP Goals: Employment
“What they will accomplish this year”
“What they will accomplish this year”
General Employment Goals:
- [Student] will complete a resume and participate in a mock interview with at least 80% accuracy by the end of the semester.
- [Student] will successfully complete a job shadow or internship in a field of interest, as measured by 90% task completion and positive supervisor feedback.
- [Student] will identify 3 job roles that match their interests and abilities, using a career inventory and discussion with staff.
Extensive Support Needs Employment Goals:
- [Student] will complete a 3-step job task (e.g., folding towels, stocking shelves) with visual or verbal prompts in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
- With picture prompts, [Student] will punch in and out of a mock time clock with 90% independence by the end of the school year.
- With picture prompts, [Student] will punch in and out of a mock time clock with 90% independence by the end of the school year.
“Steps to get there”
Activities to Support Transition: Employment
“Steps to get there”
“Steps to get there”
Through the Careers class, staff will provide direct instruction in job acquisition, interviewing, and job maintenance.
(NAME) will be provided opportunities to complete job shadows and try-outs in areas of interest by Workability coach.
A Workplace Competency assessment will be completed by student through facilitation by job coach.
Student will be provided opportunities to attend job fairs by counseling center.
Staff will provide resources and instruction on ADA related accommodations at work.
Team will provide 2-3 job shadowing experiences in the building industry to help (NAME) prepare for part-time work.
Staff will provide instruction and support in completing applications and interviewing skills.
The life skills instructor will teach (NAME) how to utilize O*Net to help him further determine employment options in the animal care field.
Arrange visits to workplaces to observe various job roles and routines.
Provide real-world experience through short-term jobs or internships.
Practice creating resumes, cover letters, and participating in mock interviews.
Focus on communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and workplace etiquette.
Use tools to identify strengths, preferences, and suitable career paths.
Provide on-site support and guidance to build confidence and skill.
Build experience and skills in less pressured environments.
Use structured routines to teach multi-step tasks (e.g., sorting mail, packaging items).
Practice repetitive tasks using vocational task boxes (e.g., folding towels, assembling kits).
Teach students to follow picture-based or video modeling task schedules.
Practice using cleaning tools, washing tables, or organizing supplies under supervision.
Sort materials, collect bins, and track data on charts with staff support.
Shelving books using alphabetical or numeric cues, with a visual prompt system.
Visit multiple worksites (e.g., grocery, pet store, hospital laundry) with a job coach to perform 1-2 basic tasks.
Create roles where students can contribute with high structure and consistency, such as:
- Stocking shelves
- Folding clothes
- Bagging items
Incorporate AAC devices or visual communication boards during work tasks and social interactions.
